1.14. Vector
Vector
In after sections, vectors will be used for composition of rotation, so let's explain in the range used there.
In dynamics, not only magnitude but the quantity with magnitude and direction is called vector.
Velocity, acceleration, force, and rotation is the vector. Vectors are expressed as the length of an arrow with the direction.
The direction of an arrow indicates the direction in which acts, and the length of it indicates the magnitude.
Additionally, the vector can be only thought with its length and direction regardless its position. Since the vector doesn't consider its position, you can think the effect by moving parallel.
Vectors can be combined. Combine means to be able to add and subtract vectors.
Addtion and Subtraction of the vector
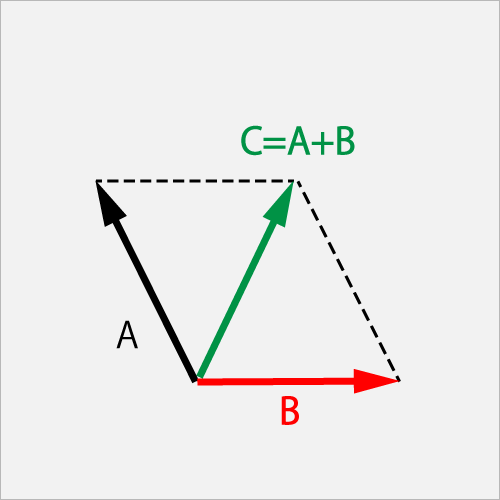
Addtion of vectors A and B is indicated by the diagonal length of the parallelogram made from these vectors.
Addtion of "the vector A with the direction and length" and "the vector B with the direction and length"
becomes "the C which is a vector A + B with the direction and length".
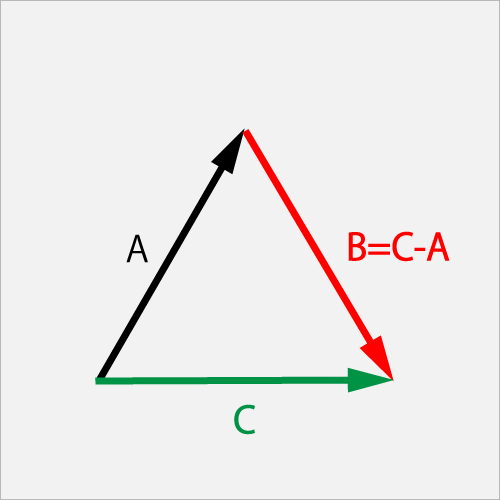
Subtraction of the vector A from the vector C is indicated by the B that is a vector "C - A", it indicates the line segment connecting from the arrow of vector A to the arrow of vector C, it changes the vector A to the vector C.