Part 4. Tactics against Various Rubberers (Service)
4.1. Observe the Opponent
Detecting what your opponent is thinking is an important element that can not be missed in order to compete. The success or failure of 70% of service and 50% of recieve is determined by it.
There are two important points to observe.
The one is how to focus your eyes on the object.
The other point is to remember how far the opponent is away from a fixed point such as the center line on the table, to read and understand the changing intention of the opponent.
4.1.1. How to focus your eyes on objects
Miyamoto Musashi, who is the famous Japanes sword master states "How to distribute eyes in battle" in "The book of Five Rings: The Book of Water". Briefly introduce,
< Reference literature > Modern translation:Coen Nishiumi English translation:Michael Brase ⌈ The book of Five Rings ⌋ IBC Publishing Inc. January 5, 2012 page56.
"In battle it is important to quickly discern things in the distantce, an to see things up close as if further away."
"Knowing that what you see is indeed the enemy's sword, you must not in the least be absorbed by that sward."
"Without moving the eyes, you must be able to see to both sides."
"This cannot be easily accopmlished when hard presses. You tain yourself to make constant use of the eyes in this way."
When observing the opponent, I interpret and use this eyes distribution specifically as follows.
Looking at the right side corner of the opponent coat with the left eye, and the left side with the right eye, you will notice one crossing point appears. Observe the opponent in this state.
If you are conscious of the way of focusing eyes and can communicate the standing position and intention of the opponent to the brain with it, the brain will be able to process in parallel and handle various things simultaneously.
4.1.2. How to observe the oppoent
4.1.2.1. Service
When you serve, the opponent changes its standing position according to the situation. In order to capture it, it is necessary to decide a fixed point somewhere and to determine a certain position. I will mention the items to be checked below, so I would like you to observe your opponent staringly.
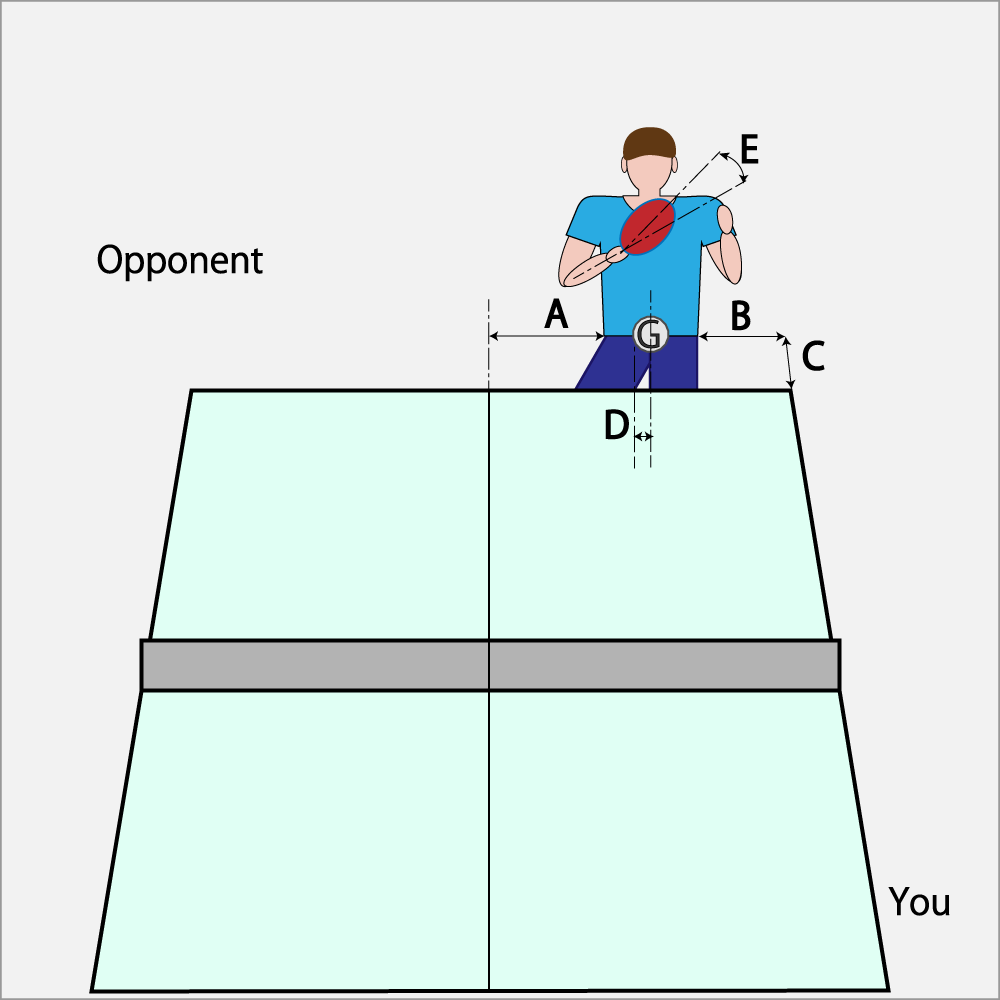
a. How close is the normal standing position of the opponent stands to the left and right (A, B) with respect to the center line and side lines?
b. How far away (C) is the opponent's platform from the table edge?
c. How far away (D) is the left or right of the opponent's body center from the gravity one (G)?
d. Is the opponent's racket head (E) tilting right or left, tilting forward or backward?
Based on these, it is possible to judge whether the consciousness of the opponent is on the fore side or on the back side, and it can be advantageously attacked by serving in the opposite direction or to the body center (middle).
After you know whether the opponent's consciousness is there on the forward or backward, decide whether to attack with a short serve or a long serve.
If you would serve to the backhand side at this time since you served to the forehand side at the last time, it will be no use. Based on the current information of opponent you have to determine the serve. And if it fails, you will modify the information you observed at that time.
4.1.2.2. Recieve
When the opponent is servicing, it is necessary to determine the direction in which the opponent will move after the service. As already explained in Section 1.13 "Basics of Returning Direction", when receiving the service, the first returning direction and the second returning direction have already been decided in advance, so make sure that the prior judgment is correct.
In the rally, check the standing position of the opponent and the direction of the ball you returned.
Is the opponent on the right court or on the left court? And which side is the opponent trying to move to?
However, there is a caveat here. Don't stare at whether the returned ball went in that direction. Don't be a ball walker. Make sure to release the shutter of the camera in an instant. Then, when the ball is returned, the next thing to do is to bring the body to the ball returning from the opponent and reflect the observation result in the next return direction.